Marketing strategy segmentation provides clarity in a crowded marketplace. It helps businesses identify the right audience, refine their message, and deliver marketing campaigns that resonate and convert more effectively.
Introduction
Marketing strategy segmentation offers businesses a powerful way to target audiences more precisely and achieve better results. In this guide, you’ll explore the concept, process, types, and benefits of segmentation, and how to implement it.
The Evolution of Marketing: From Mass to Personalized Approaches
In the past, most marketing campaigns followed a one-size-fits-all approach. Brands created a single message, product, or campaign and pushed it out to as many people as possible. But as customer data grew and digital channels multiplied, audiences began expecting something more personal.
Today, businesses are moving away from broad mass marketing and turning to segment-based strategies that speak directly to specific groups. This shift doesn’t just make campaigns more relevant; it also helps brands spend smarter and connect more meaningfully with customers.
What is Marketing Strategy Segmentation?
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broader target market into smaller, more homogeneous groups based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behavior, psychographics, or geography.
Segmentation plays a foundational role in a broader marketing strategy: once segments are identified, businesses can tailor messaging, product features, distribution, and engagement plans to each group. This elevates your approach from “one‐size fits all” to precise, actionable marketing.
Why is Segmentation Crucial for Modern Businesses?
When done right, segmentation helps you make every marketing dollar count. By focusing on people most likely to engage or buy, you reduce wasted effort and see stronger conversions. Customers also appreciate it when a brand “gets” them; it builds trust and loyalty. Plus, a smart segmentation strategy gives you an edge over competitors who still rely on broad, impersonal tactics.
Types of Marketing Segmentation
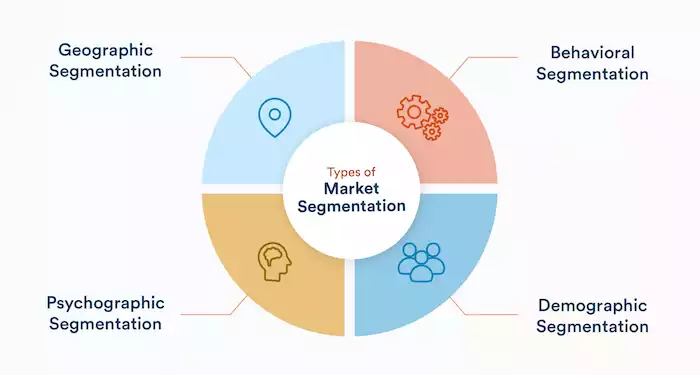
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation splits the market based on measurable attributes: for example, age ranges, gender identity, income levels, education attainment, and job roles.
A business might target women aged 25-34 with mid-income for a fashion line, or professionals earning above a threshold for a premium service. Best practice: Ensure the demographic segments are relevant to your offering and not based solely on convenience.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides the market by region, country, city size, climate zone, or cultural region. These factors affect needs and preferences.
For instance, a sunscreen brand may emphasize higher SPF in equatorial regions; a company may adapt products and messaging for urban vs rural consumers. Best practice: leverage geographic data, but combine with other variables for better precision.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation goes deeper: it groups people by how they live, what they value, their personality, or interests.
A brand might target “eco-conscious outdoorsy” individuals with messaging around sustainability. Best practice: Use psychographics to make your communication emotionally relevant and motivating.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation categorizes customers by how they behave: past purchases, brand interaction, level of loyalty, benefits they seek, and timing of usage.
An e-commerce business might create a segment for “repeat high-value purchasers” and craft a VIP experience for them. Best practice: base segments on actual behavior data and ensure measurable outcomes.
Firmographic Segmentation (B2B Specific)
For business-to-business (B2B) contexts, segmentation often uses firmographic variables: e.g., industry sector, number of employees, revenue size, and geographic location of the company.
A SaaS provider may target small businesses (10–50 employees) in certain industries versus enterprise firms (500+ employees) separately. Best practice: align the firmographic segment with the value proposition and resources for each client type.
The Process of Implementing Marketing Strategy Segmentation

Step 1: Define Your Business Objectives
Before you begin segmenting, it’s essential to clearly define what you hope to achieve. Whether your goal is to increase sales, improve retention, enhance customer engagement, or reduce costs, these objectives will directly influence how you approach segmentation and measure success.
Step 2: Identify Your Target Audience and Data Collection
Next, take time to truly understand your audience. Combine primary research, such as surveys and interviews, with secondary research from market reports or analytics to build a complete picture. Then, leverage CRM systems, Google Analytics, marketing automation tools, and survey platforms to gather demographic, behavioral, and psychographic data that will support accurate segmentation.
Step 3: Choose Segmentation Variables
Once you have enough data, choose the variables that match your goals and business model. These variables should be useful and easy to act on. For example, if keeping customers loyal is important, you can include behaviors or how often they make purchases as part of your segmentation.
Step 4: Develop Your Segments
With your variables defined, start grouping customers into clear and measurable segments. Each segment should be distinct, large enough to target effectively, and easy to identify in your data. Give each one a meaningful name, such as “Urban Young Professionals”, and build detailed profiles that describe what they value, how they behave, and what motivates their decisions.
Step 5: Develop Segment-Specific Marketing Strategies
Once you’ve defined your segments, start creating marketing strategies for each group. This means writing messages that fit each segment, choosing the best channels - like WhatsApp, email, or social media - and adjusting your products or services to match their needs. For businesses using WhatsApp to communicate and re-engage, it’s helpful to make templates and automations that feel personal and keep customers interested.
Step 6: Implement and Monitor
After your strategies are ready, launch campaigns for each segment and watch how they perform. Use dashboards to track important numbers like engagement, conversions, and customer retention. Tools such as CRM systems, marketing automation platforms like Botcake.io, and analytics dashboards will help you see how each segment responds across different channels. Botcake.io also automates and personalizes conversations with customers through tailored message flows, helping you capture and nurture potential leads more effectively.
Step 7: Evaluate and Refine
Finally, check the results to understand what works and what doesn’t. Run simple tests, ask for customer feedback, and review your data regularly. Then, use these insights to improve your segments, adjust your messages, and make your marketing strategy segmentation better over time.
Benefits of an Effective Marketing Strategy Segmentation
Increased Marketing Efficiency and ROI
Segmenting enables you to focus your budget on audiences most likely to convert, thereby reducing waste. Tailored messaging and offerings raise relevance and improve conversion rates by speaking directly to segment needs.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
When customers feel understood and served based on their segment, satisfaction increases, reinforcing loyalty. Segments allow you to build deeper relationships by delivering consistent value and engagement over time.
Improved Product Development
Insights from segments help you spot gaps or needs that are not being met in different groups, and they guide product development. When you have clear segment profiles, you can create products or services that really connect with each group instead of offering generic options.
Stronger Competitive Advantage
By targeting specific segments, you can differentiate your brand from generalist competitors. Segments enable you to serve niche markets with tailored value where competitors may not focus.
Challenges and Considerations in Marketing Segmentation
Data Overload and Analysis Paralysis
When businesses gather too much data without a clear direction, decision-making can quickly become overwhelming. It’s important to establish well-defined metrics, build insightful dashboards, and focus on turning information into practical, actionable insights.
Over-Segmentation vs. Under-Segmentation
Creating too many micro-segments can stretch your resources and make campaigns less cost-effective, while having too few can make your messages feel general and unclear. The key is to find a balance between detail and scale so you get the best results.
Dynamic Nature of Segments
Since customer behavior, preferences, and market conditions are always changing, your segments should never stay the same. You should regularly review, test, and adjust them so that your marketing efforts remain relevant and work well over time.
Resource Allocation and Implementation Costs
Effective segmentation needs careful planning, which includes collecting data, using the right tools, analyzing results, and creating campaigns for each segment. Make sure your budget covers these steps, and focus on the segments that are most likely to give the best returns.
Real-Life Examples of Successful Marketing Segmentation
E-commerce Brands
E-commerce platforms often segment their shoppers into categories such as “first-time buyers,” “repeat high-spenders,” or “abandoned-cart users.” By doing so, they can tailor WhatsApp re-engagement templates and email flows that match each group’s behavior and preferences, creating more personalized shopping experiences.
A consumer goods company may launch both premium and economy product lines to appeal to different market segments. By targeting high-income and budget-conscious customers separately - and aligning branding, pricing, and distribution - they can maximize reach and brand relevance across audiences.
SaaS Companies
A SaaS provider might design one onboarding journey for small businesses with 1–10 employees and another for large enterprises with 500 or more. Each path comes with distinct pricing, messaging, and levels of customer support to ensure that every segment receives the right experience for its scale and needs.
Service-Based Businesses
Service-based companies, such as consultancies, often segment their clients by growth stage, such as startups versus established firms. This allows them to design customized service packages and WhatsApp engagement flows that reflect each client’s goals, challenges, and level of maturity.
Future Trends in Marketing Segmentation

Hyper-Personalization and AI-Driven Segmentation
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are enabling more advanced, real-time segmentation. By combining behavioral data, intent signals, and engagement patterns, AI helps marketers optimize micro-segments dynamically and deliver highly relevant messages with precision. Besides that, Botcake AI helped Kingsport increase its 13% conversion from phone to messaging, which is a successful case you can see.
Micro-Segmentation and Niche Marketing
Micro-segmentation takes personalization to an entirely new level by dividing audiences into much smaller, highly specific groups - or even individual users. Through this approach, brands can craft ultra-targeted messages that truly resonate, as they speak directly to each customer’s unique needs, interests, and motivations.
Ethical Considerations and Data Privacy
As segmentation becomes more detailed and data-driven, businesses also need to give greater attention to ethics and compliance. It’s not just about reaching the right audience but doing so responsibly. That means maintaining transparency, securing user consent, and handling data with care to strike a healthy balance between personalization and privacy protection.
Conclusion
To thrive in modern marketing, businesses must understand who their audience is and how to reach them effectively. Marketing strategy segmentation turns that understanding into growth, and with Botcake.io, you can automate, personalize, and optimize every interaction effortlessly.